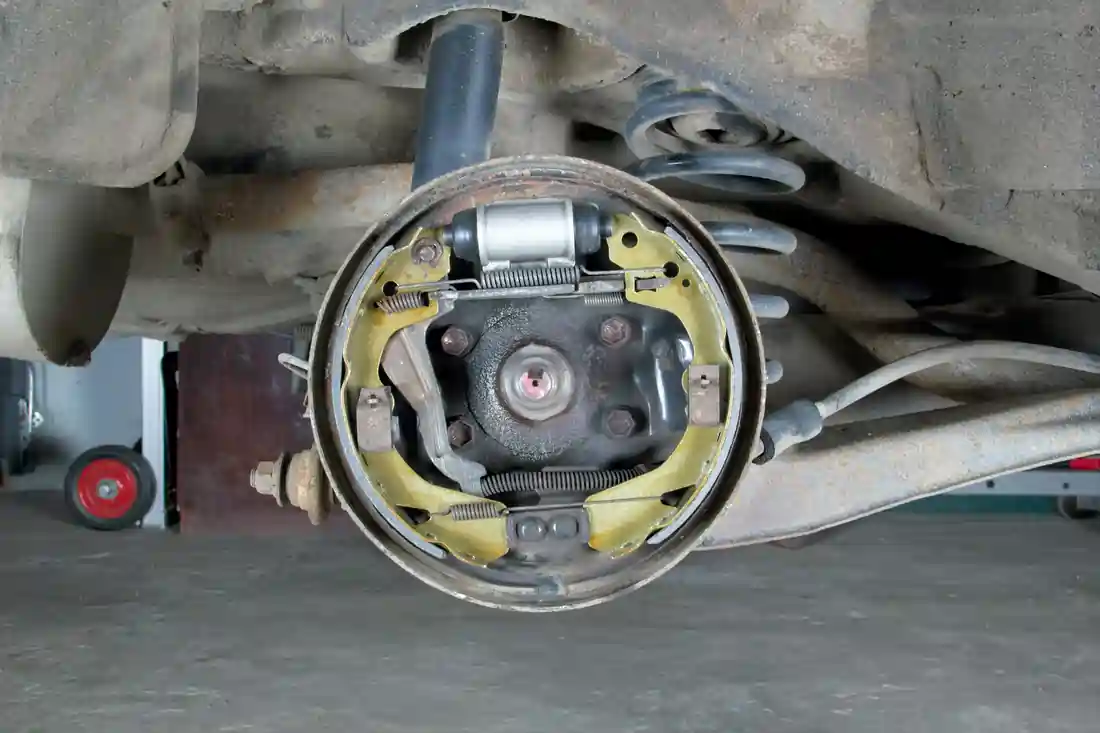
When your car needs repairs, do you know who to trust—an auto mechanic or a technician?
The difference matters more than you might think.
Understanding the distinction between a technician and an auto mechanic can be crucial.
Both roles are vital in maintaining the health and performance of vehicles, yet they differ in terms of responsibilities, skills, and tools.
This article aims to clarify these differences and help you decide which professional you might need for your car repair needs.

Budgeting for Car Maintenance
Whether you’re working with a mechanic or a technician, keeping up with routine car maintenance can save you money in the long run. Understanding how to create a car maintenance budget can help you avoid costly repairs down the line.
For helpful tips, check out our guide on saving money with a car maintenance budget.
Creating a car maintenance budget is just one way to stay ahead of costly repairs, but it’s also important to know who’s handling your vehicle. Understanding the differences between an auto mechanic and a technician can help you make informed decisions about your car’s care.
Definition and Basic Responsibilities

Both auto technicians and mechanics play essential roles in the auto maintenance industry.
Their day-to-day tasks can vary significantly. Here’s a closer look at what each role entails:
Mechanic Performs Basic Care and Maintenance
Mechanics are primarily responsible for maintaining and repairing vehicles. They handle routine services such as oil changes, tire rotations, and brake inspections, ensuring that vehicles remain in optimal working condition. Depending on the vehicle’s type and mileage, they also conduct inspections and tests to identify any underlying issues. For a deeper understanding of why oil changes are crucial for your car’s longevity, check out the importance of regular oil changes.
In addition to performing repairs, mechanics provide detailed maintenance recommendations and cost estimates to customers. They take the time to explain any proposed work, helping customers understand what’s needed to keep their vehicles running smoothly. For a deeper look at how regular maintenance affects your car’s health, check out our guide on understanding your car’s maintenance schedule. Throughout the process, mechanics also document all maintenance and repairs, creating a comprehensive history for each vehicle.

Mechanics ensure that their tools and equipment are in good condition, as this is crucial for performing accurate and efficient repairs. Their tasks may include more specialized work, such as wheel bearing replacement, checking brake systems, and replacing fluids, all aimed at ensuring vehicle reliability and safety.
Technicians Specialize in High-Tech Problem Solving
Technicians are responsible for advanced diagnostic and repair work, often relying on modern technology and specialized tools. A key part of their role involves deciphering diagnostic codes from vehicles, which helps them pinpoint specific issues. For example, technicians are often called upon to diagnose and resolve issues related to a check engine light, ensuring that the problem is identified accurately. Once identified, they design detailed repair plans that mechanics can follow to ensure the problem is resolved efficiently.
In addition to their diagnostic expertise, technicians use advanced computer systems and tools to further investigate and diagnose issues. They are skilled at identifying the sources of vehicular failures, particularly in electronic and computerized systems. For more information, visit our page on auto electrical repair services to learn how these experts troubleshoot high-tech issues in modern vehicles.
While technicians perform many of the same tasks as mechanics, their focus is primarily on diagnosing and repairing more complex, technology-driven problems.
Education Paths: Mechanics vs. Technicians

The education paths for mechanics and technicians differ
Both typically rely on hands-on learning, while technicians often pursue formal education to handle more advanced, technology-driven tasks.
Mechanic Education: Hands-On Learning Through Experience
Mechanics often learn their trade through apprenticeships and on-the-job training. A high school diploma is generally sufficient to start in the field. As they work in garages, they frequently encounter problems such as oil leaks that require their expertise to resolve, especially when diagnosing issues in older vehicles.
This hands-on approach allows mechanics to develop their skills over time, mastering the art of vehicle maintenance and repair through real-world practice.
Technician Education: Formal Training for Advanced Skills
Technicians, on the other hand, require more formal education due to the technical nature of their work. Many pursue education through technical schools or obtain an associate’s degree in automotive technology. Certifications, such as ASE (Automotive Service Excellence), are essential for technicians to demonstrate their expertise. Moreover, as vehicle technology continues to evolve, technicians must engage in continuous education to stay current with the latest advancements and diagnostic tools.
Tools and Technology

The tools and technology used by mechanics and technicians reflect their different focuses.
Mechanics use traditional hand tools and equipment like wrenches and hydraulic lifts for physical repairs
While technicians focus on diagnostic tools such as scanners and multimeters to troubleshoot electronic systems.
This distinction reflects mechanics’ focus on hands-on repairs and technicians’ expertise in vehicle electronics.
Tools Mechanics Use
Mechanics rely on basic tools such as wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers. These are essential for working on the mechanical parts of vehicles, including engines, starter and alternator repair, brakes, and suspensions.
They often encounter issues related to belts and hoses, which are critical to a vehicle’s functionality. For more details on these components, visit our belts and hoses services page.
Technology Technicians Rely On
Technicians use advanced tools like diagnostic computers and specialized software to solve complex problems. They focus on engine diagnostics and complex electronic systems, using scan tools to pinpoint issues.
Skill Set and Specializations

Mechanics and technicians often specialize in specific areas of auto care, but their core skills differ.
This section highlights the key differences between mechanics’ hands-on repair skills and technicians’ expertise in vehicle diagnostics and electronics.
Mechanic Skills
Mechanics have strong mechanical abilities. They can handle routine maintenance and basic repairs. Specializations may include brake work, transmission repairs, and more. Learn about brake pad replacement.
Technician Expertise
Technicians excel at analyzing problems and interpreting diagnostic data. They are skilled in planning complex repairs, especially for vehicles with electronic systems. Some may specialize in diagnostics or automotive air conditioning, making them crucial for preparing your car’s cooling system for long summer drives.
Work Environment and Conditions

Both mechanics and technicians typically work in similar environments, but the nature of their work can differ.
This section dives into the key differences between mechanics and technicians. Mechanics get their hands dirty with repairs. Technicians use advanced tools to diagnose problems. Both roles are vital, but their focus is different. Keep reading to find out what sets them apart!
Mechanics’ Exposure to Uncomfortable Work Conditions
Mechanics work in environments that can be physically demanding and uncomfortable. Most auto repair shops are not air-conditioned, meaning mechanics often work in hot conditions. They are exposed to various contaminants, such as oils, grease, and fumes, and must work both indoors and outdoors.
Cramped workspaces are common, requiring them to maneuver into awkward positions inside vehicles like trucks and vans.
Additionally, they often deal with loud noises that can be distracting or uncomfortable, adding to the challenging work conditions they face daily.
Technicians Face Similar Work Conditions as Mechanics
Technicians face many of the same conditions as mechanics, but their work involves more time troubleshooting and diagnosing issues.
While many people believe diagnostics only involve connecting a car to a computer, it’s far more complex. The computer provides a code that helps guide the technician, but they still need to determine the underlying issue.
Unlike mechanics who focus on external parts, technicians often work inside the vehicle or engine, and even underneath it. Electrical issues, in particular, present some of the toughest challenges for technicians.
Salary and Career Prospects

The career prospects and earning potential for mechanics and technicians can vary based on their skills and experience.
This section covers career paths and pay for mechanics and technicians. Their earnings can differ, depending on skill and experience. More skills mean higher pay. Want to know who earns more? Let’s explore!
One of the most significant differences between auto technicians and mechanics is the evolving complexity of modern vehicles. Mechanics traditionally focused on hands-on repairs, dealing with mechanical systems such as engines, brakes, and transmissions. However, with advancements in car technology over the past two decades, the role of an auto technician has grown significantly more complex.
Twenty-five years ago, cars were much simpler. The work largely revolved around mechanical repairs, and knowledge of electrical systems was minimal. But today’s vehicles are equipped with cutting-edge technologies—everything from hybrid powertrains and electric vehicles (EVs) to advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and complex computerized diagnostics.
Due to this, auto technicians are now expected to be well-versed in both the mechanical and electronic systems of vehicles. They rely heavily on diagnostic tools, software, and continual learning to stay up to date with the latest technologies. This is one of the key differences between a technician and a mechanic—while both work on vehicles, technicians often focus more on the technical and electronic aspects, using diagnostic tools to pinpoint issues that wouldn’t have existed on older cars.
Pay and Skill Development
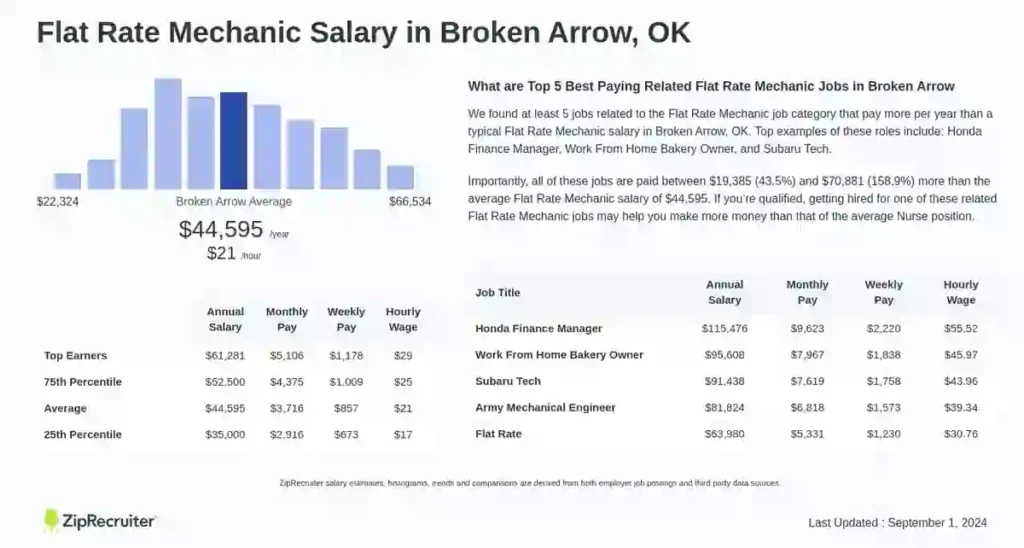
The pay scale often reflects these differences as well. General mechanics, who handle a wide range of basic repairs, might see their hourly wages peak around $25 an hour. Talented and experienced technicians, however, who have specialized knowledge in advanced vehicle systems like hybrid or electric drivetrains, can earn $40 an hour or more. For instance, in Broken Arrow, OK, flat-rate mechanics typically earn an average salary of $50,356 per year, which roughly breaks down to $24.21 per hour. You can learn more about the pay scale for flat-rate mechanics in Broken Arrow ( Flat Rate Mechanic Salary in Broken Arrow, OK ).
This wage difference reflects the specialized skills required for modern vehicles. With the rapid pace of change in the automotive industry, constant learning and self-improvement have become essential. Many mechanics and technicians regularly attend training sessions, obtain certifications, and participate in manufacturer-led education programs. As technology continues to advance, their ability to adapt and continue learning plays a crucial role in their career development.
General mechanics might see their wages cap at a certain level, while specialized technicians, such as those who handle complex engine repairs, can command higher salaries. Learn more about how engine repair services can impact your vehicle’s performance and the type of expertise required for these repairs.
In summary, the key difference between mechanics and technicians lies in the scope of work and focus on technology. While both are essential to the automotive industry, auto technicians often work more with the electronics, diagnostics, and advanced systems of today’s vehicles, requiring them to continually evolve their skills to keep up with new technology.
Unique Insights and Future Trends

The automotive industry is constantly evolving, and both mechanics and technicians must adapt to these changes.
This section explores how the automotive world is always changing. Mechanics and technicians need to keep up with the latest trends and tech. Adapting is key to staying ahead. Want to know how they do it? Let’s dive in!
As vehicles become more advanced, the distinction between mechanics and technicians is becoming increasingly important. Mechanics, traditionally focused on the mechanical components like engines, transmissions, and brakes, are now required to have a much broader understanding of complex systems, such as integrated sensors, autonomous driving features, and electronic controls. This has blurred the lines between mechanical and electrical repairs, pushing mechanics to expand their skill sets.
Both mechanics and technicians must adapt to advancements like catalytic converters and their crucial role in reducing emissions. For a deeper dive into this component, check out our article on the role of catalytic converters.
On the other hand, automotive technicians are specialists who focus on diagnosing issues using high-tech tools and computer systems. Modern cars now have dozens of onboard computers and interconnected networks that manage everything from engine performance to driver-assist systems. As these systems evolve, technicians must keep pace with software updates, new diagnostic tools, and troubleshooting procedures that are far more intricate than traditional repairs.
Both roles must also adapt to the growing prominence of electric and hybrid vehicles, which feature completely different powertrains from conventional gas-powered vehicles. This shift requires mechanics and technicians to understand battery management, electric drivetrains, and high-voltage safety protocols, all of which are critical for servicing these vehicles safely and efficiently.
Beyond the technical aspects, mechanics and technicians are also facing changes in the tools and equipment they use. With the rise of automated diagnostic systems and AI-driven maintenance tools, many tasks that were once done manually can now be assisted or completed by advanced software. Staying current with these tools is essential, as it can significantly reduce repair time and improve accuracy.
In summary, mechanics and technicians are no longer just about fixing physical parts but also mastering digital diagnostics, working with high-tech systems, and understanding emerging technologies. This evolution demands continuous learning and adaptation to ensure they can meet the demands of modern vehicle repairs and provide top-notch service to customers.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between an auto technician and a mechanic is essential for anyone seeking auto repair services. For more insights into how to budget for these services, explore our guide on saving money with a car maintenance budget. For reliable auto care in Broken Arrow, visit T Autocare Takedown, your trusted local auto repair shop.
For more insights into modern car maintenance, check out these additional articles:
Understanding Hybrid and Electric Vehicle Maintenance – Learn how hybrid and electric vehicles require specialized care.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles – Explore how self-driving cars could shape the future of car repair and maintenance.
For top-notch auto repair Broken Arrow services, contact T Autocare Takedown at 1501 W Detroit St, Broken Arrow, OK 74012. Call us at (539) 367-3738 to schedule your service today!
By understanding these distinctions, you can make informed decisions about your auto care needs and ensure your vehicle receives the best possible service. Whether you need a skilled mechanic for routine tasks or a knowledgeable technician for complex diagnostics, T Autocare Takedown is here to help with all your car repair needs.












