Understanding how to diagnose a check engine light can save you time and money, and help keep your vehicle in optimal condition.
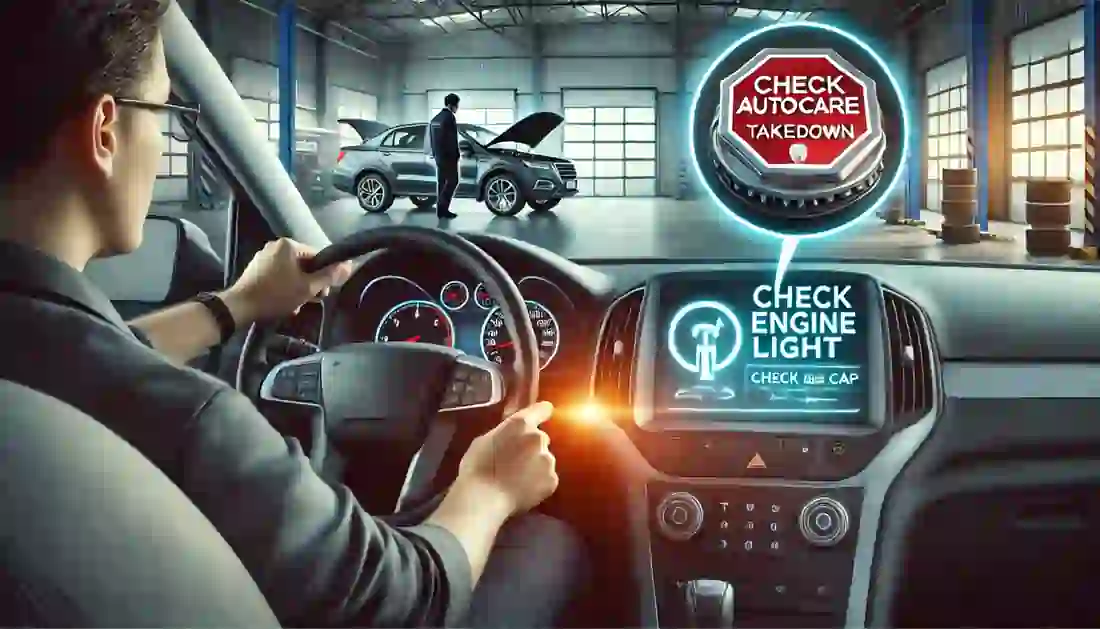
The check engine light (CEL) can be a source of anxiety for many drivers, but it doesn’t always signal a catastrophic problem. Here’s a comprehensive guide to diagnosing a check engine light.
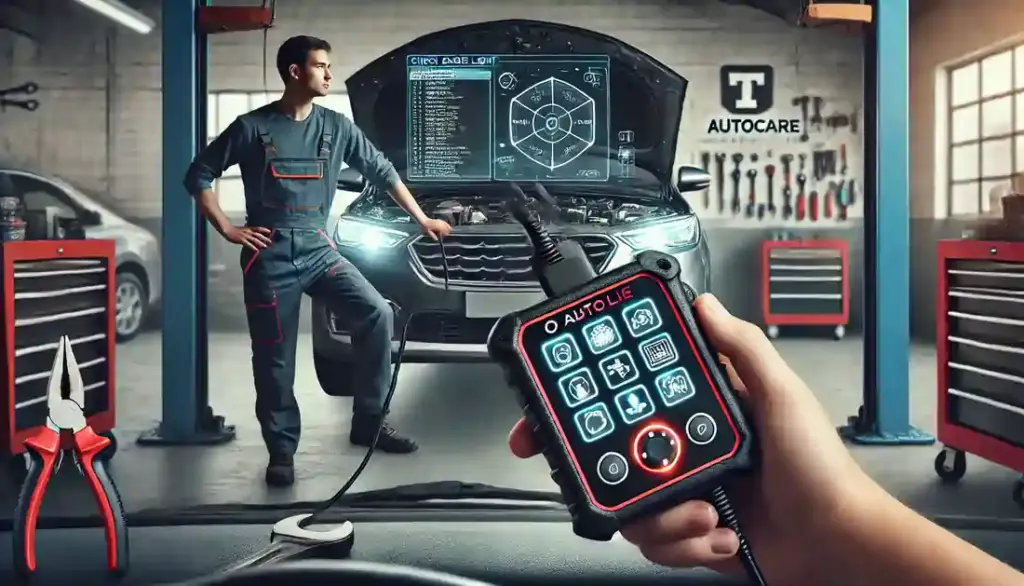

Understanding the Check Engine Light
The check engine light is part of your vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) system. It monitors your car’s performance and can signal anything from a loose gas cap to more serious engine problems. Ignoring the light can lead to bigger issues, so it’s crucial to address it as soon as possible. If left unchecked, what might start as a small problem can turn into costly repairs. For more insights into common engine issues and how to prevent them, check out our guide on common engine issues and how to prevent them.
Common Causes of a Check Engine Light
Faulty Oxygen Sensor: This sensor measures the amount of unburned oxygen in your car’s exhaust. If it’s not working, it can reduce fuel economy and increase emissions. Replacing a bad sensor is essential to keep your car running efficiently. Learn more about maintaining key sensors in your engine with our guide on understanding the role of engine sensors.
Malfunctioning Spark Plugs or Wires: Spark plugs ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine, and faulty ones can lead to misfires, which impact engine performance and fuel efficiency. Replacing worn-out spark plugs can keep your engine running smoothly.
Mass Airflow Sensor Issues: This sensor controls the amount of air entering the engine. If there’s a problem, it can reduce fuel efficiency and affect performance. Cleaning or replacing the mass airflow sensor may solve the issue.
Catalytic Converter Problems: The catalytic converter helps reduce harmful emissions from your car’s exhaust. If it fails, your car may suffer from poor performance, higher emissions, and decreased fuel efficiency.
Battery or Charging Issues: A low battery or charging problem can also trigger the check engine light. Ensuring your battery is healthy is key to preventing electrical issues that can affect engine performance.
Steps to Diagnose the Problem
Check for Simple Issues First: Begin by checking the gas cap, as it’s one of the easiest problems to fix. If it’s loose, tighten it and see if the check engine light goes off after a few drives. Sometimes, a quick fix like this can solve the problem.
Use an OBD-II Scanner: If the light stays on, use an OBD-II scanner to read the diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs). You can purchase one or visit an auto parts store where they often provide free use of a scanner. This tool is essential for diagnosing the exact issue with your vehicle. For more guidance on maintaining your vehicle’s systems, check out our article on engine diagnostics.
Connecting the Scanner: Locate the OBD-II port, which is usually under the dashboard near the steering wheel. Plug in the scanner and follow the device’s instructions to read the codes.
Interpreting the Codes: Each DTC refers to a specific issue. You can look up the code in your vehicle’s manual or online to find out what it means and what might need to be fixed.
Check for Additional Symptoms: Beyond the check engine light, pay attention to other symptoms like unusual sounds, rough idling, or lower fuel efficiency. These signs can help you narrow down the problem, even before the scanner reads the code.
Common Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
P0171: System Too Lean
This code indicates that the air-fuel mixture in your engine is too lean, meaning there’s too much air and not enough fuel. Common causes include a vacuum leak, faulty oxygen sensor, or mass airflow sensor issue. Addressing this issue promptly is important for engine performance. For more on maintaining engine sensors, check out our guide on understanding the role of engine sensors.
P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected
A P0300 code signals that multiple engine cylinders are misfiring. This can lead to reduced performance, poor fuel economy, and potential engine damage. Faulty spark plugs, ignition coils, or fuel delivery issues are often the culprits. To learn about preventing engine misfires, read our guide on regular engine tune-ups.
P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
This code points to an issue with your catalytic converter, which reduces harmful emissions. A malfunctioning converter may be caused by engine misfires or bad oxygen sensors. If your car is showing this code, it’s time to inspect the exhaust system. For more on exhaust-related issues, see our guide on how to diagnose a noisy exhaust system.
P0440: Evaporative Emission Control System Malfunction
This code indicates a malfunction in the evaporative emission control system, which prevents fuel vapors from escaping. Causes may include a loose or damaged gas cap or a faulty purge valve. Fixing this issue helps lower emissions. For more on keeping your fuel system healthy, check out our fuel system services.
P0455: Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Large Leak)
A P0455 code is similar to P0440 but refers to a large leak in the system. A common cause is a loose or missing gas cap, but it could also indicate a cracked hose or a larger system failure. It’s important to fix this to prevent fuel vapor leaks and improve your car’s emissions performance.
When to Seek Professional Help
If tightening the gas cap or using the OBD-II scanner doesn’t fix the problem, it may be time to see a professional. Some issues, like a bad catalytic converter, need expert help. A failing converter can cause problems with your car’s performance and emissions. Learn more in our guide on catalytic converters. Serious engine problems might also need professional attention to avoid costly repairs.
We can help: Sensor Replacment
Preventative Measures
Regular car maintenance can help prevent check engine light problems. This includes getting oil changes on time, replacing spark plugs and filters, and making sure all sensors and parts are working well. Keeping up with these tasks can save you from bigger issues down the road. Learn more about keeping your car in shape with our guide on regular engine tune-ups.
We do Engine Tune Ups: Broken Arrow Automotive Tune-Ups & Maintenance
Keep Your Vehicle Running Smoothly
Figuring out a check engine light doesn’t have to be hard. By knowing the common causes and using the right tools, you can find and fix many problems yourself. For more tips on keeping your car in top condition, check out our preventative maintenance guide.
For more complex problems, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from your local auto repair Broken Arrow shop to ensure your vehicle remains in top condition.
T Autocare Takedown
1501 W Detroit St
Broken Arrow, OK 74012
(539) 367-3738
Useful Links How to Diagnose Check Engine Light:
- The 13 Most Common Reasons For A Check Engine Light (FIXD)
- Check Engine Light: Common Causes and How To Fix It (AAA)
- How to Self Diagnose your Check Engine Light (Ace Auto Parts)
- Check Engine Light: What to check first, repair options (Samarins)
- Check Engine Light Just Came On? Follow These 3 Tips (NAPA Know How)