When it comes to the smooth operation of your car, you might not think about your oxygen sensors. In fact, many drivers aren’t even aware of what these little sensors do. However, they play a crucial role in keeping your engine running efficiently and ensuring that you’re not polluting the environment more than necessary. So, what exactly do oxygen sensors do, and why should you care? Let’s break it down in a simple and casual way.
What Are Oxygen Sensors?
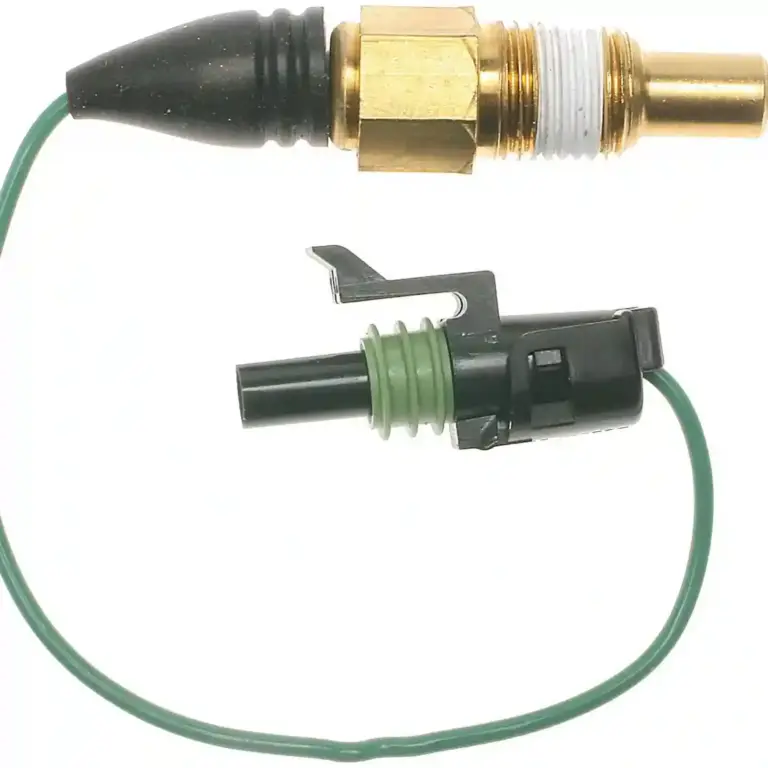
Oxygen sensors (commonly referred to as O2 sensors) are small, but vital, components located in your car’s exhaust system. Their main job? To measure the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gases leaving the engine. This information is sent to your car’s engine control unit (ECU), which adjusts the air-to-fuel ratio for optimal combustion.
Essentially, O2 sensors help make sure your engine runs efficiently, and they also play a role in reducing harmful emissions. If your oxygen sensors aren’t working properly, it can lead to problems like poor fuel economy, increased emissions, or even engine damage.
Where Are Oxygen Sensors Located?
Most modern vehicles have multiple oxygen sensors. Typically, you’ll find one sensor located before the catalytic converter and one after it. The sensor in front of the catalytic converter monitors the air-to-fuel ratio, while the one after it checks the converter’s efficiency.
Some cars, especially those with V6 or V8 engines, might have more than two sensors, but their purpose remains the same: to monitor and improve your car’s performance.

How Do Oxygen Sensors Work?
Oxygen sensors are made of materials like zirconium or titanium, and they measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. They work by comparing the oxygen level in the exhaust to the oxygen level in the outside air.
If there’s too much oxygen in the exhaust gases, it means your engine is running lean (too much air and not enough fuel). If there’s too little oxygen, your engine is running rich (too much fuel and not enough air). The sensor sends this data to your car’s ECU, which adjusts the air-to-fuel mixture to bring it back to the optimal level.
This process happens constantly while you’re driving. Every few seconds, the sensors are sending data to the ECU to ensure the best possible engine performance.
Gear Quest created great video on O2 sensors. They cover how they came to be as well as how they work. It’s worth taking the ten minutes to watch the video.
What Happens When the O2 Sensor Fails?
When an oxygen sensor fails, it can’t provide accurate data to the ECU. This can result in several issues:
Poor Fuel Economy: If the ECU can’t adjust the air-to-fuel ratio correctly, your car may end up using more fuel than it should, reducing your fuel efficiency.
Increased Emissions: A faulty oxygen sensor can cause your car to release more harmful emissions, which can lead to failing emissions tests and doing damage to the environment.
Rough Idle or Engine Misfire: Without proper oxygen sensor readings, your engine may run erratically, causing it to idle rough or even misfire.
Check Engine Light: One of the most common signs of a failing oxygen sensor is the check engine light coming on. If you notice this light, it’s a good idea to get your car checked by a mechanic.
Can You Drive with a Bad Oxygen Sensor?
In short, yes, but it’s not recommended for long-term driving. A failing oxygen sensor can lead to more significant issues down the road, such as damaging your catalytic converter. Catalytic converters are expensive to replace, so it’s better to fix a faulty oxygen sensor sooner rather than later. Plus, driving with a bad sensor will cost you more in fuel, and nobody likes paying more at the pump.
Why Oxygen Sensors Are Important
You might be wondering: why are these sensors so important? Well, they do more than just keep your engine running smoothly. Here’s why they matter:
- Better Fuel Efficiency: With accurate data from the oxygen sensors, your car’s ECU can fine-tune the air-to-fuel mixture for better fuel efficiency. A well-tuned engine burns fuel more effectively, saving you money in the long run.
- Reduced Emissions: Oxygen sensors help your car run cleaner by ensuring that the combustion process is as efficient as possible. When your engine burns fuel properly, it produces fewer harmful emissions, which is better for the environment.
- Engine Longevity: Running too rich or too lean for an extended period can put unnecessary strain on your engine, leading to potential damage. Oxygen sensors help prevent that by ensuring the engine operates within the correct parameters.
- Emissions Testing: In many places, cars must pass emissions tests to stay road-legal. A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can cause you to fail these tests, and repairs can be costly.
How Long Do Oxygen Sensors Last?
Most oxygen sensors last around 60,000 to 100,000 miles, depending on the make and model of your vehicle. However, they can wear out sooner due to contamination from engine oil, coolant, or other exhaust gases. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of oxygen sensors can prevent more significant issues down the road.
Replacing an Oxygen Sensor
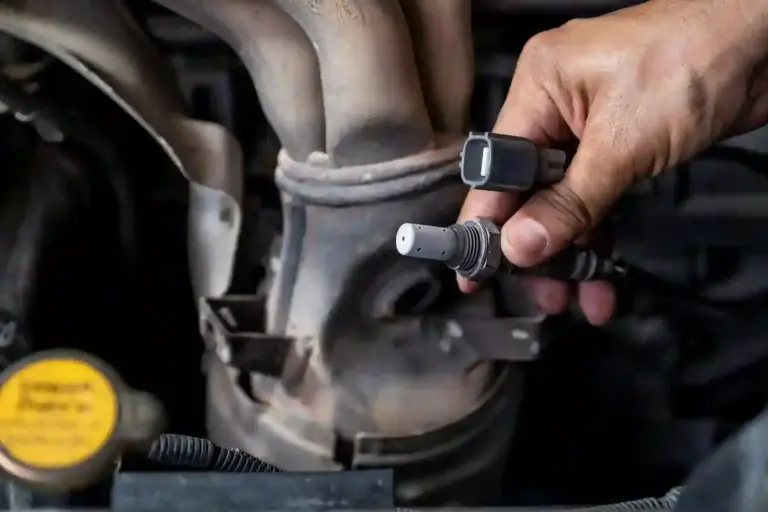
Replacing a faulty oxygen sensor is relatively simple and inexpensive compared to other engine components. Most mechanics can swap out a bad sensor in under an hour. However, it’s essential to get the right sensor for your car’s make and model. Using the wrong sensor can lead to more problems down the road.
If you’re handy with tools and comfortable working on your car, you might even be able to replace the sensor yourself. Just make sure you have the proper tools, and consult your vehicle’s manual for guidance.
Signs It’s Time
to
Replace Your Oxygen Sensor
Here are some common signs that your oxygen sensor might need replacing:
- Check Engine Light: As mentioned earlier, a check engine light is one of the most common indicators of a faulty oxygen sensor.
- Poor Fuel Efficiency: If you notice you’re filling up more often, it could be a sign that your O2 sensor is failing.
- Rough Running or Misfires: When the air-to-fuel ratio is off, your engine might run rough, stall, or misfire.
- Emissions Test Failure: If your car fails an emissions test, a bad oxygen sensor could be to blame.
Conclusion
Oxygen sensors might be small, but they play a big role in your car’s overall performance and efficiency. From helping you save on fuel to reducing emissions and preventing engine damage, these sensors are essential for modern vehicles. If you notice signs of a failing oxygen sensor, don’t ignore them. Getting them replaced can save you money and headaches in the long run. Plus, your car and the environment will thank you for it!
So, the next time that check engine light comes on, remember: it could be those little oxygen sensors doing their job and letting you know it’s time for some maintenance.